酶和酶复合体设计和改造
Project Profile 项目简介
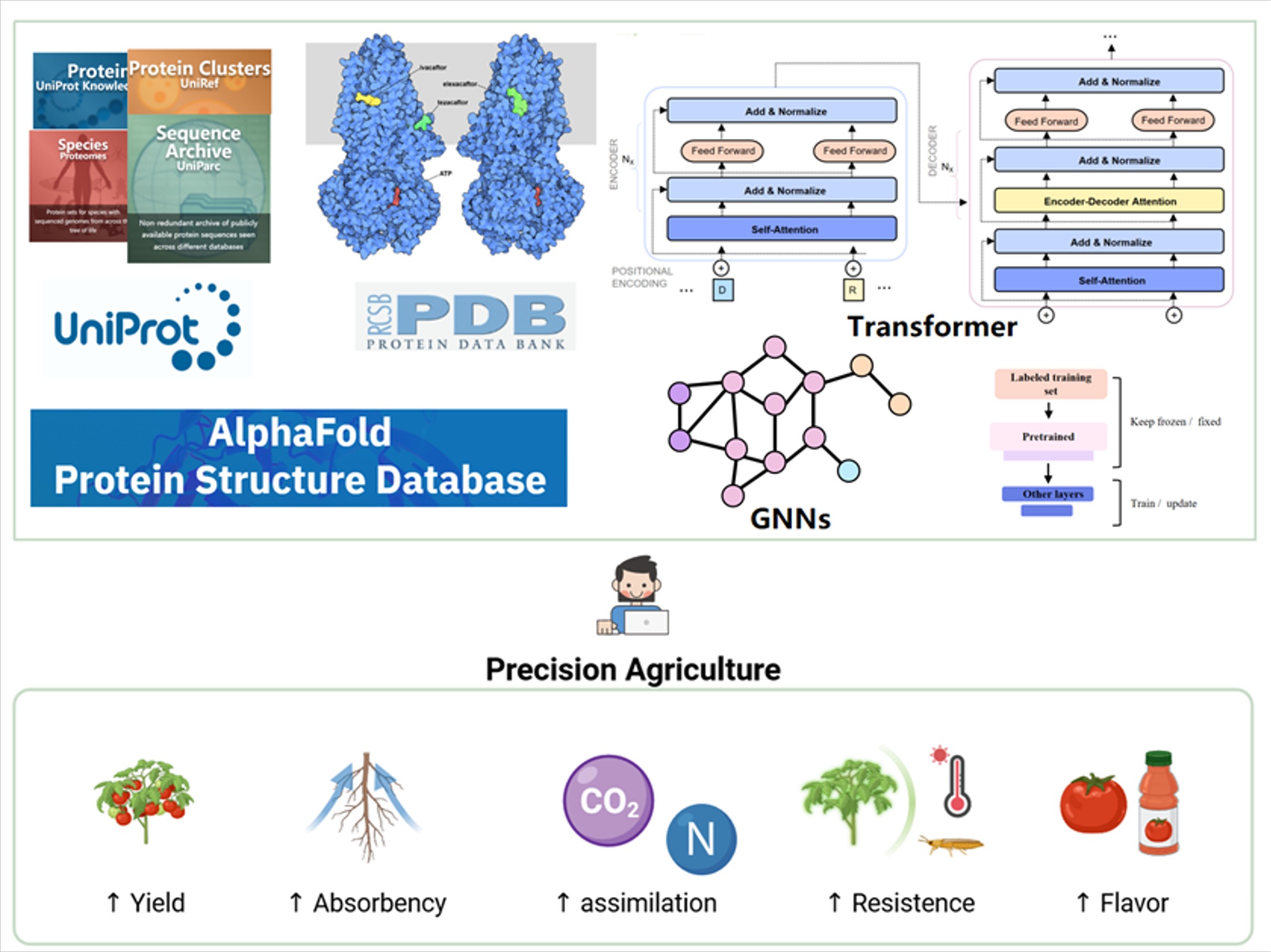
By leveraging protein information from public databases such as UniProt and PDB, and integrating deep learning techniques (e.g., Transformer models, graph neural networks), we conduct rational design and reconstruction of key metabolic enzymes and multi-enzyme complexes in plants. Using AI-assisted approaches for mutational site selection, substrate channel optimization, and interface engineering—combined with high-throughput directed evolution and enzyme activity screening platforms—we aim to significantly improve catalytic efficiency, substrate specificity, and thermal stability. These advancements enable the reprogramming of carbon fixation, nitrogen fixation, and secondary metabolite pathways in plants, thereby enhancing the production of natural products and constructing efficient synthetic biological factories (Ye et al., Journal of Genetics and Genomics).
通过学习来自公共数据库如UniProt、PDB等的蛋白质信息,并结合深度学习技术(如Transformer、图神经网络等)等手段,对植物体内关键代谢酶及其多酶复合体进行理性设计与重构。通过AI辅助的突变位点筛选、底物通道优化和界面工程,结合高通量定向进化和酶活性筛选平台,实现酶催化效率、底物专一性及热稳定性的大幅提升,进而重编程植物的固碳、固氮、次生代谢物的代谢通路,提升天然产物产量并构建高效合成生物工厂(Ye et al. Journal of Genetics and Genomics)。
代表性成果
Ye X., Qin K., Fernie A. R. & Zhang Y. (2024). Prospects for Synthetic Biology in 21(St) Century Agriculture. Journal of Genetics and Genomics
Project Figure 项目图